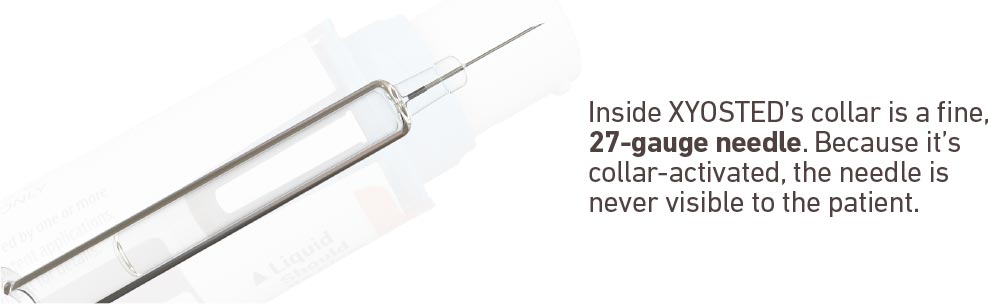
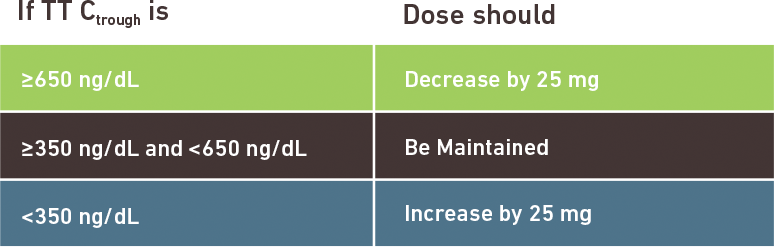
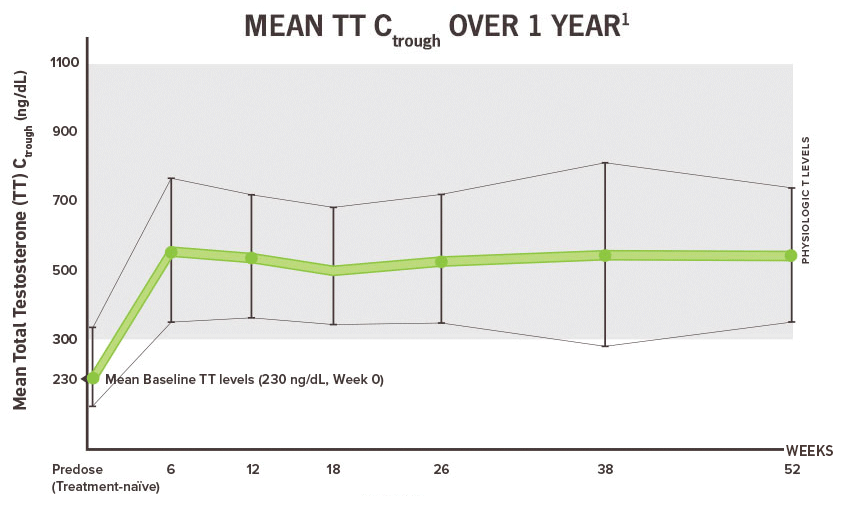
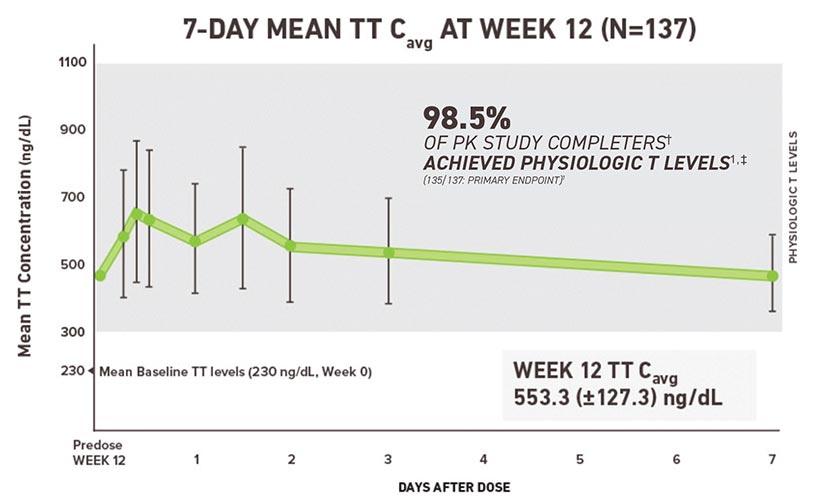
Terms of Use
PLEASE READ THESE TERMS OF USE CAREFULLY!
BY ACCESSING THIS SITE, YOU ACKNOWLEDGE THAT YOU HAVE READ THESE TERMS OF USE, AND UNDERSTAND AND AGREE TO ABIDE BY THEM.
This Terms of Use Agreement (this “Agreement”) describes the terms and conditions applicable to your use of any and all of Antares Pharma, Inc.’s and/or its affiliates (collectively “Antares”) or Antares co-branded websites. If you do not agree to the terms and conditions of this Agreement, please do not use this website. Your use of certain pages or services within this website may be subject to additional terms and conditions. Before being given access to these pages or services, you will be asked to indicate whether you agree to be bound by the additional terms and conditions. If you agree to be bound, you will be given access to the page or service. If you do not agree to be bound, you will not be given access to the page or service.
Antares may at any time revise or modify this Agreement or impose new conditions for use of this website. Such changes, revisions or modifications shall be effective immediately upon notice to you, which may be given by any means including, without limitation, posting on the website or by e-mail. Any use of the website by you after such notice shall be deemed to constitute acceptance of such changes, revisions or modifications. Antares may modify its services at any time.
THIS WEBSITE DOES NOT PROVIDE MEDICAL OR PROFESSIONAL SERVICES ADVICE.
The content on this website is intended to be a general information resource in regard to the subject matter covered, and is provided solely on an “AS IS” and “AS AVAILABLE” basis. You are encouraged to confirm the information contained herein with other sources, and to review the information carefully with your professional health care provider. Antares is not engaged in rendering medical or similar professional services or advice via this website, and the information provided is not intended to replace medical advice offered by a physician. If you desire or need such services or advice, you should consult a professional health care provider. You should not construe Antares’s publication of this content as an endorsement by Antares of the views expressed herein, or any warranty or guarantee of any strategy, recommendation, treatment, action, or application of medication or preparation made by the author of the content.
Scope of Use
Antares invites you to view, use and download a single copy of this website for your informational, personal, non-commercial use. Except as otherwise provided on this page, no part of any content or software on this website may be copied, downloaded or stored in a retrieval system for any other purpose, nor may it be redistributed for any purpose, without the express written permission of Antares. You understand that Antares may discontinue, change, or restrict your use of this website for any reason without notice.
This website is for use by U.S. residents only. By using this website, you represent that you are at least eighteen (18) years old and a United States resident.
No Warranties
ALL CONTENT ON THIS WEBSITE IS PROVIDED TO YOU ON AN “AS IS” “AS AVAILABLE” BASIS WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, ACCURACY, AND NON-INFRINGEMENT. ANTARES MAKES NO WARRANTY AS TO THE ACCURACY, COMPLETENESS, CURRENCY, OR RELIABILITY OF ANY CONTENT AVAILABLE THROUGH THIS WEBSITE. YOU ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR VERIFYING ANY INFORMATION BEFORE RELYING ON IT. USE OF THE WEBSITE AND THE CONTENT AVAILABLE ON THE WEBSITE IS AT YOUR SOLE RISK. ANTARES MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES THAT USE OF THE WEBSITE WILL BE UNINTERRUPTED OR ERROR-FREE. YOU ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR TAKING ALL NECESSARY PRECAUTIONS TO ENSURE THAT ANY CONTENT YOU OBTAIN FROM THE WEBSITE IS FREE OF VIRUSES.
The above exclusions may not apply in jurisdictions that do not allow the exclusion of certain implied warranties.
Limitation of Liability
YOUR USE OF THE WEBSITE OR ANY CONTENT ON THE WEBSITE IS AT YOUR OWN RISK. ANTARES SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY LIABILITY, WHETHER BASED IN CONTRACT, TORT, STRICT LIABILITY OR OTHERWISE, FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR SPECIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF OR IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH ACCESS TO OR USE OF THE WEBSITE, EVEN IF ANTARES HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO RELIANCE BY ANY PARTY ON ANY CONTENT OBTAINED THROUGH THE USE OF THE WEBSITE, OR THAT ARISES IN CONNECTION WITH MISTAKES OR OMISSIONS IN, OR DELAYS IN TRANSMISSION OF, INFORMATION TO OR FROM THE USER, INTERRUPTIONS IN TELECOMMUNICATIONS CONNECTIONS TO THE WEBSITE OR VIRUSES, WHETHER CAUSED IN WHOLE OR IN PART BY NEGLIGENCE, ACTS OF GOD, WAR, TERRORISM, TELECOMMUNICATIONS FAILURE, THEFT OR DESTRUCTION OF, OR UNAUTHORIZED ACCESS TO THE WEBSITE, OR RELATED INFORMATION OR PROGRAMS.
Indemnification
If you violate any terms of this Agreement or if you misuse this website, you agree to defend, indemnify and hold harmless Antares, its officers, directors, employees, agents and licensees from any and all liability including, without limitation, costs, expenses and attorneys’ fees that arise out of or are related to your violation or misuse.
User Submissions
Certain areas of this website enable you to submit e-mails, or otherwise provide feedback or information to Antares.
You agree that by submitting content:
- that, if you are a health care professional, you will not submit any information that would directly identify a patient or any information for which you do not have all necessary consents or authorizations to disclose;
- you will only submit content that complies with applicable law, and will not submit content that is abusive, defamatory, obscene, infringing, threatening, repetitive, or otherwise inappropriate, or that contains any viruses or other software that may adversely affect the operation of another’s computer;
- you understand and agree that such content that is submitted to a feedback page, will be deemed non-confidential; and
- you grant to Antares the irrevocable right to use, copy, modify, publish, perform, transmit and display such content via any media in accordance with this User Agreement, and waive any moral rights you may have in such content. Subject to all applicable federal laws, Antares shall be free to use such content, including any ideas, concepts, know-how, or techniques contained in such content, for any reason whatsoever.
Trademarks
The trademarks, logos, and service marks (collectively, the “Trademarks”) displayed on this website are registered and unregistered Trademarks of Antares and others. Nothing contained in this website should be construed as granting, by implication, estoppel, or otherwise, any license or right in and to the Trademarks. Unauthorized use of any Trademark may be a violation of federal and state trademark laws.
Copyright
This website is protected by United States’ and foreign copyright laws. Except for your informational, personal, non-commercial use as authorized above, you may not modify, reproduce or distribute the design or layout of the website, or individual sections of the design or layout of the website or Antares logos without Antares’s written permission.
Information, News and Press Releases
The website may contain information, news and/or press releases about Antares. While this information was believed to be accurate as of the date it was prepared, Antares disclaims any duty or obligation to update this information, news or any press releases. Information about companies other than Antares contained in the news, press releases or otherwise, should not be relied upon as being provided or endorsed by Antares.
Links
This Antares website may contain links to websites operated by other parties. The linked sites are not under the control of Antares, and Antares is not responsible for the content available on any other Internet sites linked to this website. Such links do not imply Antares’s endorsement of material on any other site and Antares disclaims all liability with regard to your access to such linked websites. Antares provides links to other Internet sites as a convenience to users, and access to any other Internet sites linked to this website is at your own risk.
Unless otherwise set forth in a written agreement between you and Antares, you must adhere to Antares’s linking policy as follows: (i) any link to an Antares website must be a text only link clearly marked “Antares WEBSITE,” (ii) the appearance, position and other aspects of the link may not be such as to damage or dilute the goodwill associated with Antares’s names and trademarks, (iii) the link must “point” to the root domain name of the Antares website and not to other pages within the website, (iv) the appearance, position and other attributes of the link may not create the false appearance that your organization or entity is sponsored by, affiliated with, or associated with Antares, (v) when selected by a user, the link must display the website on full-screen and not within a “frame” on the linking website, and (vi) Antares reserves the right to revoke its consent to the link at any time and in its sole discretion.
Security
This website may require you to register or obtain a password prior to permitting access to the website or certain services available on this site. You are responsible for maintaining the confidentiality of your registration information and password, and for all uses of your password, whether or not authorized by you.
Location, Governing Law and Arbitration
This website is operated by Antares. The law of the State of Delaware shall govern these terms and conditions, without reference to its choice of law rules. Antares makes no representation that the information in the website is appropriate or available for use in other locations, and access to this website from territories where the content of this website may be illegal is prohibited. Those who choose to access this website from other locations do so on their own initiative and are responsible for compliance with applicable local laws.
Any controversy or claim arising under or related to this User Agreement or Antares’s products and/or services shall be settled by binding arbitration in accordance with the commercial rules of arbitration of the American Arbitration Association. Any such controversy or claim shall be arbitrated on an individual basis, and shall not be consolidated in any arbitration with any claim or controversy of any other party. The arbitration shall be conducted in the State of Delaware, and judgment on the arbitration award may be entered by any court of competent jurisdiction. Either you or Antares may seek any interim or preliminary relief from a court of competent jurisdiction in the state of Delaware, necessary to protect the rights or property of you or Antares pending the completion of arbitration.
Violations and Additional Policies
Antares reserves the right to seek all remedies available at law and in equity for violations of these Terms of Use, including the right to block access from a particular Internet address to the website.
Use of Information
Antares reserves the right, and you authorize Antares, to the use and assignment of all information regarding your use of this website and all information provided by you in any manner consistent with this User Agreement and applicable federal law.
Securities Laws
This website may include statements concerning Antares’s operations, prospects, strategies, financial condition, future economic performance and demand for Antares’s products or services, as well as its intentions, plans and objectives, that are forward-looking statements. These statements are based upon a number of assumptions and estimates which are subject to significant uncertainties, many of which are beyond our control. When used on the website, words like “anticipates,” “expects,” “believes,” “estimates,” “seeks,” “plans,” “intends” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements designed to fall within securities law safe harbors for forward looking statements. The website and the information contained herein does not constitute an offer or a solicitation of an offer for sale of any securities. None of the information contained herein is intended to be, and shall not be deemed to be, incorporated into any of Antares’s securities-related filings or documents.
Questions
If you have any questions about these Terms of Use, please contact Antares at +1 (609) 359 3020. For all other inquiries, please contact us through the relevant product, support or Antares website.
Privacy Policy
Effective Date: 1/1/2020 Last Updated: 4/29/2025
APPLICABILITY
This Privacy Policy (“Policy”) describes how Halozyme, Inc. and its subsidiaries and affiliates (“Halozyme”) collects, uses, and discloses personal information it obtains both (i) online through www.halozyme.com and any other website that posts this Policy (collectively, the “Websites”), and (ii) offline in the course of providing our products and services. This Policy does not apply to information we collect from job applicants, employees, or contractors. To view our Job Applicant Privacy Policy, click here, and to view our Consumer Health Data Privacy Policy, click here.
INFORMATION WE COLLECT
The type of personal information we collect about you depends on your relationship with us. It also depends on how you interact with us.
Contact information and account information. We may collect your name, email address, physical address, and phone number. We may also collect your employer’s name and your business contact information. From users of our disposal kit program, we also collect login and password information. We may also collect clinical trial participant identifiers.
Demographic information. We may collect information such as your date of birth and age as well as your zip code and state.
Eligibility and health information. We may collect information about your health, diagnosis, or treatment as well as health insurance information. We may also collect insurance or financial assistance eligibility information.
Employment information. We collect information about healthcare providers, including their specialties, professional affiliations, state license data, and NPI numbers.
Submitted information. We collect any other information you voluntarily provide to us. For example, if you submit a medical inquiry online or choose to provide a testimonial about your treatment journey.
Site usage information. We collect information about the browser you are using, the sites you came from and where you visit when you leave us, as well as the actions you make while on the Websites. We may also collect information about your operating system, IP address, and device identifiers. For additional information regarding our use of cookies and other tracking technologies, please see our Cookies & Ad Settings policy.
WE COLLECT INFORMATION IN A VARIETY OF WAYS
We collect information directly from you. We collect information if you contact us (directly or through our service providers such as our call center), attend an event, or request a product or service from us. We also collect information from you if you sign up for email communications, or otherwise request information from us. We may also collect information about you that you post on our social media sites or via literature monitoring as part of pharmacovigilance.
We collect information passively. We may use several common tracking tools to collect information automatically about your use of the Websites and your interaction with emails we send to you. Tracking tools include browser cookies and web beacons.
We collect information about you from others. Business partners such as healthcare providers, pharmacies, insurers, and other funding partners, may provide information about you to us as permitted by law. We may collect information about providers from public databases and using tools that allow us to match your consumer identifiers with your professional affiliation.
HOW WE USE YOUR INFORMATION
We use personal information for the business and commercial purposes outlined here:
We use information to communicate with you. We use your personal information to respond to your requests or questions. We also use it to send you updates and communicate with you about our policies and terms. We may send you surveys or request feedback for market research and product improvement.
We use the information to provide and improve our products and services. We use your personal information to improve our products, services, programs, and Websites. This includes customizing your experience with us, providing educational information, facilitating patient co-pay assistance program applications and participation, and providing disposal kits. We also use personal information to investigate adverse event reports or complaints. For providers, we may use your information to send you samples or put you in touch with requested resources.
We use information for marketing purposes. As permitted by law, we may use your personal information to let you know about new products, programs, or services through promotional communications. We also use information to provide you with newsletters or other content we think you may find interesting. We may also use your information to engage in interest-based advertising. This includes serving you with ads that we think are relevant to you based on your browsing habits or online activities.
We use information to comply with legal and regulatory requirements. We may use your personal information in order to comply with regulatory reporting obligations, such as reporting adverse events.
We use information to protect ourselves and others. We use your personal information to protect our company. This includes to identify fraud or secure our systems.
We use information as otherwise permitted by law (or as we may notify you).
HOW WE DISCLOSE INFORMATION
Below, we have explained the categories of entities with whom we might disclose your personal information.
We disclose information within our family of companies. This includes our parent company as well as current and future subsidiaries and affiliates.
We disclose information with vendors and others who perform services on our behalf. We may disclose all categories of personal information with trusted service providers. These include companies who help us deliver our products and services to you. For example, those that help us run the Websites, send communications, and receive and process adverse event and quality control reports.
We disclose information to our business partners. This may include healthcare providers, pharmacies, insurers, and other funding partners. We only make these disclosures as permitted by law.
We may disclose information when necessary to comply with the law or to protect ourselves. We will transfer information to respond to a court order or subpoena. We will also disclose it if a government agency or investigatory body requests it, or as required to comply with our reporting obligations to regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration. We may also share information as necessary to protect against legal liability or prevent fraud.
We may transfer information with any successor to all or part of our business. If all or part of our business is sold or otherwise involved in a corporate transaction, we may transfer personal information as part of that transaction to the successor business.
We may disclose information otherwise with your consent or for other reasons which we may describe to you.
Additionally, Halozyme does not sell personal information for monetary value; however, under certain U.S. state laws, some of our digital advertising and analytics activities may constitute a “sale” or “sharing” of personal information to our third party advertising and analytics partners for purposes of cross-context behavioral advertising (i.e., targeted advertising).
YOU HAVE CERTAIN PRIVACY CHOICES AND MAY HAVE CERTAIN RIGHTS
You can opt-out of certain marketing communications. To stop receiving our marketing emails please email us at the email address noted below or follow the “unsubscribe” instructions in any marketing email you receive from us. If you opt-out of marketing emails you may continue to receive emails from us related to your relationship with us as permitted by law.
You can control cookies and tracking tools. Your browser may give you the ability to control cookies and other tracking tools. Certain browsers can be set to reject browser cookies. We use performance and analytics partners including but not limited to Google Analytics, which employ cookies and similar technologies on the Websites, so that we can compile statistics about site use. To opt-out of Google Analytics, please visit: https://tools.google.com/dlpage/gaoptout. The Websites do not respond to Do Not Track browser signals. In addition, as discussed below, depending on your state of residence, you may have the right to opt-out of targeted advertising activities.
If you live in California, Connecticut or New Jersey, or a state with a similar law which applies to Halozyme, you have certain additional legal rights. These rights may include the following.
- Right to Confirm / Access / Know. You may have the right to request access to personal information that we hold about you, including details relating to the ways in which we use and share your information. Residents of California have the right to know the categories of personal information we have collected about them, the categories of sources from which the personal information is collected, the categories of personal information sold, shared, or disclosed, the business or commercial purpose for selling, sharing, or disclosing the personal information, and the categories of third parties to whom we have sold, shared or disclosed their personal information.
- Right to Delete. You may have the right to request that we delete personal information we maintain about you.
- Right to Correct. You may have the right to request that we correct inaccurate personal information we maintain about you.
- Right of Portability. You may have the right to receive a copy of the personal information we hold about you and to request that we transfer it to a third party.
- Right to Withdraw Consent to Processing of Sensitive Personal Information. You may have the right to withdraw your consent to the processing of (or limit the use and disclosure of) your sensitive personal information, unless legal or contractual reasons prevent you from doing so.
- Right to Opt-Out. You may have to opt-out of certain uses of your personal information such as for (i) targeted advertising, (ii) “sale” or “sharing” for cross-context behavioral advertising, or (iii) profiling or automated decision-making activities that result in a legal or similarly significant effect on you. Please note that if you visit our Websites with the Global Privacy Control opt-out preference signal enabled, if required by law, we will respond to that request in a frictionless manner, meaning we will automatically treat this as a request to opt-out of "sale," "sharing," or targeted advertising for the device or browser from which you broadcast the signal. Learn more about the Global Privacy Control here.
- Right to Appeal. You may have the right to appeal our decision if we decline to process your request in part or in full. You can do so by replying directly to our denial. If you are not satisfied with our response to your appeal, you may contact your state Attorney General.
How it works. You can exercise these rights by emailing us at privacy@halozyme.com, calling us at 1-844-855-4256, or using another method specified in this Policy. When you submit your request, depending on the type of request, we may seek to verify your identity before honoring your request. We do this by matching the information you provide with information we already have about you. Please note that these rights are not absolute, they may apply only in certain circumstances and, in certain cases, we may decline your request as permitted by law. For example, in Connecticut, these rights apply only to consumer health data. We will not discriminate against you for exercising your privacy rights.
Third party agents. If you are submitting a request on behalf of an eligible resident, we may ask for additional information to verify your identity. This may include providing proof that you are registered with the Secretary of State to act on someone’s behalf or proof of a power of attorney.
NOTICE AT COLLECTION FOR CALIFORNIA RESIDENTS
In addition to offering certain consumer rights (set forth in the section above), California law requires us to make the following additional disclosures to consumers regarding our privacy practices.
In the last twelve (12) months, the personal information Halozyme has collected falls into the following categories of personal information as defined under California law:
i. Identifiers and personal information categories listed in the California Customer Records statute, such as name, signature, address, phone number, email address, online identifier, unique identifier, IP address, date of birth, medical information and health insurance information. We collect this category of information directly from you, automatically from your use of the Websites, from our business partners, and from publicly available sources.
ii. Commercial information, such as records of personal property, products or services purchased, obtained, or considered, or other purchasing or consuming histories or tendencies. We collect this category of information directly from you and from our business partners.
iii. Internet or other similar network activity, such as browsing history, search history, information on a consumer's interaction with a website, application, or advertisement. We collect this category of information automatically from your use of the Websites.
iv. Geolocation data, such as IP address. We collect this category of information automatically from your use of the Websites.
v. Sensory data, such as recordings of customer service and pharmacovigilance calls. We collect this category of information automatically.
vi. Professional or employment-related information, such as employment information and contact information of providers.
vii. Inferences drawn from other personal information, such as a profile reflecting a person’s preferences, characteristics, predispositions, behavior, and aptitudes. We create this category of information based on other information we collect about you.
viii. Sensitive personal information, such as health data and username and password. We collect health data directly from you, automatically from your use of the Websites, from our business partners, and from publicly available sources. We collect usernames and passwords from users of our disposal kits. Generally, we do not use sensitive personal information to infer characteristics about individuals, but we may draw conclusions about your health status based on your health information.
To the extent we maintain de-identified personal information, we commit not to attempt to re-identify it, except as permitted by law.
We keep these categories of personal information as long as necessary or relevant for the purposes for which they were collected or for which we have a legitimate business purpose. We determine the retention period for each category of personal information based on (i) the length of time we need to retain the information to achieve the business or commercial purpose for which it was collected, (ii) any legal or regulatory requirements applicable to such information, (iii) internal operational needs, and (iv) any need for the information based on an actual or anticipated investigation or litigation.
Halozyme uses and discloses this personal information as described earlier in this Policy. In the past 12 months, we have disclosed each of the above categories of personal information to our service providers, and we have disclosed the following categories of personal information to third party business partners for purposes of providing our products and services, including facilitating patient assistance programs, and to regulatory bodies for purposes of complying with legal and regulatory obligations: Identifiers and personal information categories listed in the California Customer Records statute, Commercial information, and Sensitive Personal Information.
Halozyme does not sell personal information, however, as previously discussed, certain of our digital analytics or advertising activities may constitute a “sharing” of personal information for cross-context behavioral advertising under California law. In particular, we may share the following categories of personal information with third party advertising and analytics partners for the purposes of data analytics and cross-context behavioral advertising: Identifiers and personal information categories listed in the California Customer Records statute, Commercial information, Internet or other similar network activity, Geolocation data, and Inferences drawn from other personal information. California residents have the right to opt-out of this sharing as described above. We do not have actual knowledge that we collect, sell, or share the personal information of California residents under the age of 16.
OUR WEBSITES ARE NOT INTENDED FOR CHILDREN
Our Websites are meant for adults. We do not knowingly collect personally identifiable information from children under 16 without parental consent. If you are a parent or legal guardian and think your child under 16 has given us information without your permission, please contact us and we will delete the information.
WE USE REASONABLE SECURITY MEASURES
We use reasonable security measures as required by relevant law that are designed to protect the security of your personal information. You should be aware, however, that no Internet transmission is fully secure. In particular, website and email transmission may not be 100% secure, and you should therefore take care in deciding what information you send to us through these channels.
WE ARE BASED IN THE UNITED STATES
Information we collect may be stored and processed in the United States. The Websites and our products and services are intended for people who are in the United States. If you live outside of the United States, you understand and agree that your personal information may be transferred to the United States. The United States may not afford the same level of protection as the laws in your country. By submitting your information, you agree to the processing of your personal information in the US.
THIRD PARTY SITES
Our Websites may include links to third party sites. We do not control these third parties. This Policy does not apply to the privacy practices of those websites. Please read the privacy policy of other websites carefully. We are not responsible for the practices of these third party sites.
HOW TO CONTACT US
If you have questions about this Policy or our privacy practices, or if you wish to exercise your privacy choices or rights, you may contact us as follows:
By Mail:
Halozyme Therapeutics
Attn: Legal Department
12390 El Camino Real
San Diego, CA 92130
By Email: privacy@halozyme.com
Via Website: https://halozyme.com/contact/
By Phone: 844-855-4256
WE MAY UPDATE THIS POLICY
We may make changes or updates to this Policy. We will notify you of any material changes to this Policy as required by law. Changes will also be posted on our Websites. Please check our Websites periodically for updates.